Hydrochlorothiazide
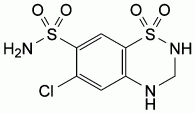
C7H8ClN3O4S2
Mr 297.7
[58-93-5]
DEFINITION
6-Chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulphonamide
1,1-dioxide.
Content: 98.0 per cent to
102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance: white or almost white, crystalline
powder.
Solubility: very slightly soluble in water,
soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It
dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
First
identification: B.
Second
identification: A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet
and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test
solution. Dissolve
50.0 mg in 10 ml of 0.1 M
sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100.0 ml with water R.
Dilute 2.0 ml of this solution to 100.0 ml with 0.01 M
sodium hydroxide.
Spectral
range:
250-350 nm.
Absorption
maxima: at
273 nm and 323 nm.
Absorbance
ratio: A273/A323 = 5.4 to 5.7.
B. Infrared
absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: hydrochlorothiazide CRS.
►
If the
spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to
be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum volume of ethanol R1,
evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
◄
C. Thin-layer
chromatography (2.2.27).
Test
solution. Dissolve
50 mg of the substance to be examined in acetone R
and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent.
Reference
solution (a). Dissolve
50 mg of hydrochlorothiazide CRS in acetone R
and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent.
Reference
solution (b). Dissolve
25 mg of chlorothiazide R
in reference solution (a) and dilute to 5 ml with reference
solution (a).
Plate: TLC
silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: ethyl
acetate R.
Application: 2 µl.
Development: over a path of 10 cm.
Drying: in a current of air.
Detection: examine in ultraviolet light at
254 nm.
System
suitability: reference
solution (b):
— the
chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: the principal spot in the
chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to
the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference
solution (a).
D. Gently
heat about 1 mg with 2 ml of a freshly prepared 0.5 g/l solution
of chromotropic
acid, sodium salt R in a cooled mixture of 35 volumes
of water R
and 65 volumes of sulphuric
acid R. A violet colour develops.
TESTS
Acidity or
alkalinity. Shake
0.5 g of the powdered substance to be examined with 25 ml of water R
for 2 min and filter. To 10 ml of the filtrate, add 0.2 ml of 0.01 M
sodium hydroxide and 0.15 ml of methyl
red solution R. The solution is yellow. Not more than
0.4 ml of 0.01 M
hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the
indicator to red.
Related
substances. Liquid
chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent
mixture. Dilute
50.0 ml of a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R
and methanol R
to 200.0 ml with phosphate
buffer solution pH 3.2 R1.
Test
solution. Dissolve
30.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 ml of a mixture of
equal volumes of acetonitrile R
and methanol R,
using sonication if necessary, and dilute to 20.0 ml with phosphate
buffer solution pH 3.2 R1.
►
Reference
solution (a). Dissolve
15 mg of hydrochlorothiazide CRS and 15 mg of chlorothiazide CRS (impurity A) in 25 ml of
a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R
and methanol R,
using sonication if necessary, and dilute to 100 ml with phosphate
buffer solution pH 3.2 R1. Dilute 5 ml of this
solution to 100 ml with the solvent mixture.
◄
Reference
solution (b). Dilute
1.0 ml of the test solution to 50.0 ml with the solvent mixture.
Dilute 5.0 ml of this solution to 20.0 ml with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size:
l = 0.1 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary
phase: octadecylsilyl
silica gel for chromatography R (3 µm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile
phase A: to 940 ml of phosphate
buffer solution pH 3.2 R1 add 60.0 ml of methanol R
and 10.0 ml of tetrahydrofuran R
and mix;
— mobile
phase B: to a mixture of 500 ml of methanol R
and 500 ml of phosphate
buffer solution pH 3.2 R1 add 50.0 ml of tetrahydrofuran R
and mix;
|
Time (min) |
Mobile
phase A (per
cent V/V) |
Mobile
phase B (per
cent V/V) |
|
0 - 17 |
100
→ 55 |
0 →
45 |
|
17 - 30 |
55 |
45 |
|
30 - 35 |
55 →
100 |
45 →
0 |
|
35 - 50 |
100 |
0 |
Flow rate: 0.8 ml/min.
Detection: spectrophotometer at 224 nm.
Equilibration: with mobile phase A for at
least 20 min.
Injection: 10 µl; inject the solvent
mixture as a blank.
Retention
time:
impurity A = about 7 min; hydrochlorothiazide = about 8 min.
System
suitability: reference
solution (a):
— resolution:
minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurity A and hydrochlorothiazide; if necessary, adjust slightly
the composition of the mobile phase or the time programme of the linear
gradient.
Limits:
— impurities
A, B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in
the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— total:
not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained
with reference solution (b) (1 per cent);
— disregard
limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram
obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Chlorides (2.4.4):
maximum 100 ppm.
Dissolve
1.0 g in 25 ml of acetone R
and dilute to 30 ml with water R.
Prepare the standard using 5 ml of acetone R
containing 15 per cent V/V of water R
and 10 ml of chloride
standard solution (5 ppm Cl) R.
Loss on
drying (2.2.32):
maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at ►105◄ °C.
Sulphated
ash (2.4.14):
maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve
0.120 g in 50 ml of dimethyl
sulphoxide R. Titrate with 0.1 M
tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in 2-propanol, determining the
end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20)
at the 2nd point of inflexion. Carry out a blank titration.
1 ml of
0.1 M
tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in 2-propanol is equivalent to
14.88 mg of C7H8ClN3O4S2.
IMPURITIES
Specified
impurities: A, B, C.
A. chlorothiazide,
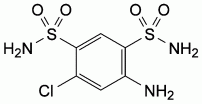
B. 4-amino-6-chlorobenzene-1,3-disulphonamide
(salamide),
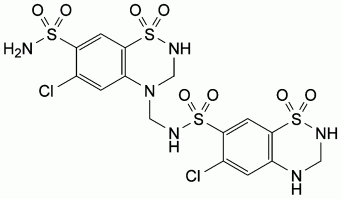
C. 6-chloro-N-[(6-chloro-7-sulphamoyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazin-4-yl
1,1-dioxide)methyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulphonamide
1,1-dioxide.